Designing Online Learning Communities: Lessons from Ekşisözlük
Fırat Soylu [fsoylu@indiana.edu]
Indiana University
Department of Instructional Systems Technology
Abstract
English
Lack of student participation and intrinsic motivation in online learning environments is a challenge to instructional design. There are some online communities which overcome this challenge by attracting participants from diverse backgrounds to engage, learn, and share information within their context. Eksisozluk, an online collaborative dictionary, is one of these communities. In this study we inquire for the unique characteristics of Eksisozluk that can be applied to online learning environments to increase student motivation and participation. Study data were collected through online surveys and one-to-one interviews. Study findings show that the unique characteristics of Eksisozluk include a community history, individual identities evolved through participation, an effective search facility, and representation of multiple perspectives. In the implications for practice section, we discuss the identified characteristics and address some strategies to implement them in learning environments.
Turkish
İnternet Tabanlı Öğretim Ortamları Tasarımı: Ekşisözlük'ten Çıkarılabilecek Dersler
İnternet tabanlı uzaktan eğitim ortamlarında öğrencilerin katılımını arttırmak ve motive olmalarını sağlamak eğitimsel tasarım açısından önemli zorluklar teşkil etmektedir. Öte yandan, birçok insan İnternet üzerinde eğitimsel amaç gütmeyen kominitelerde geniş çaplı bilgi paylaşımında bulunup, her konuda tatmin edici öğrenme tecrübeleri edinebilmektedir. İçeriği katılımcılar tarafından oluşturulan, İnternet tabanlı bir sözlük olan Ekşisözlük bu kominitelerden biri. Bu çalışma Ekşisözlük'ün İnternet tabanlı eğitim ortamlarında motivasyon ve katılımı arttırabilecek karakteristik özelliklerini saptamayı amaçlamaktadır. Çalışmada kullanılan veriler İnternet tabanlı bir anket aracılığı ile ve mulakatlar yapılarak toplandı. Verilerin incelenmesi sonucunda Ekşisözlük'ün önemli karakteristik özelliklerinin kominite geçmişi, kalıcı sanal kimlikler, verimli bir arama motoru ve çeşitli bakış açılarının topluluk içinde sunulma imkanları olduğu ortaya çıktı. Uygulamaya yönelik incelemeler bölümünde Ekşisözlük'ün belirlenen özellikleri tartışılıp, bu özelliklerin öğrenme ortamlarında nasıl uygulanabilecekleri konusu ele alınmaktadır.
1. Introduction
Started as an individual enterprise in 1999, today, Eksisozluk is one of the most popular websites for Turkish speaking people around the world. Developed as an interactive, informal online dictionary, Eksisozluk gets about 20 000 hits per day. It has about 13 000 active members and hundreds of thousands of readers. Eksisozluk is a significant online community because of its enormous and diverse content, number of active participants, and unique structure.
This study aims at finding the design principles in Eksisozluk that motivate the users' participation. I also seek to deconstruct Eksisozluk, whether it is dominantly a "learning community" or a community for socialization and entertainment.
2. Study Rationale
Students' motivation for participation is a problem in online learning environments. Although online learning environments provide different mediums supported by tools for interaction and contribution, students may not be sufficiently motivated to participate and use the tools and mediums provided at a desired level. In some online communities, community members are highly motivated to participate and contribute to the collectively generated content. Eksisozluk is one of these communities. Inquiring which of the design principles and characteristics of Eksisozluk can be applied to online learning environments to increase students' motivation and participation would be an important contribution to our understanding of online learning environment design.
Technological innovations do not necessarily bring innovations in online learning (Huang, 2002). It is rather philosophical and methodological considerations that can yield to innovations in online learning. Eksisozluk has a unique design and a management philosophy that yields to high participation rates among its contributors. Although Eksisozluk is not a formal medium for learning, it provides a medium in which learning is an emergent theme as a result of participants' ordinary interactions within the community.. Participants are intrinsically motivated to be engaged with what the community has to offer and learn from these interactions. In this study, we focused on (a) the ways that authors utilize Eksisozluk and their underlying purposes and (b) the characteristics of Eksisozluk that influence authors' motivation to contribute. The study findings may inform online learning environment design endeavors, especially in regards to philosophical and the methodological issues.
3. Theoretical Framework
What is an Online Community?
Not every group of people is a community. Selznik (1996) defined seven necessary characteristics of a community: history, identity, mutuality, plurality, autonomy, participation and integration. These characteristics address the formation of a community specific culture which entails ways of communication, rituals, common goals and shared goals. Ownership is another characteristic that distinguishes a group of people from a community. In a community members identify themselves with the community and feel ownership of the community specific culture and common goals.
With the advance of communication and transportation technologies, the term "community" has transformed into new meanings. Before, a community was dependent on the physical location of its members. Members who were located far away from the center of the community had weaker connections, due to communication difficulties (Preece & Krichmar, 2003). Technological innovations enabled new ways creating communities. Computer-mediated communications enabled people to communicate regularly without significant costs and without being in close proximity (Etzioni & Etzioni, 1999).
At a workshop took place in the ACM HCI conference, in 1996, the followings were determined as the core attributes of an online community (Whittaker, Issacs, & O'Day, 1997, p. 137).
-
Shared goals, interests, needs, or activities that provide the primary reason for belonging to the community
-
Repeated active participation and often intense interactions, strong emotional ties, and shared activities occurring among participants
-
Shared resources and policies for determining access to those resources
-
Reciprocity of information, support and services among members
-
Shared context (social conventions, language, protocols).
-
Differentiated roles and reputations
-
Awareness of membership boundaries and group identity
-
Initiation criteria
-
History and long duration
-
Events or rituals
-
Shared physical environment
-
Voluntary membership.
Etzioni and Etzioni (1999) pointed out the two basic attributes of an online community: bonding and culture. A community, generally, is not a chain of one-on-one relationships; it is rather a web of affect-laden relationships that encompasses a group of individuals. This is bonding. Secondly, a community should have a set of shared values, and historical identity. This is shortly the culture of the community.
What are the characteristics of a "good online community"?
Godwin (1994) lists nine principles of virtual community design:
-
Use software that promotes good discussions.
-
Don't impose a length limitation on postings.
-
Front-load your system with talkative, diverse people.
-
Let the users resolve their own disputes.
-
Provide institutional memory.
-
Promote continuity.
-
Be host to a particular interest group
-
Provide places for children.
-
Confront the users with a crisis
In his paper "Design principles for online communities" Kollock (1998), points out three attributes of successful online communities.
-
Promotes ongoing and persistent interaction among the members
-
Individuals are able to identify each other
-
Individuals must have information about how the other person has behaved in the past.
Kollock's first and Godwin's sixth points address the same issue: continuity. Continuity of interaction is required for several reasons: As mentioned above, it was proposed in the ACM HCI conference, in 1996, that having a shared context including social conventions, language and protocols is a core attribute of the online communities (Whittaker, Issacs, & O'Day, 1997). To develop these social conventions and community specific language and protocols, the users need to have a continuous, persistent social interaction. One of the less central attributes, community specific events and rituals also emerge as a result of continuous social interaction.
Institutional memory is also a crucial attribute of successful online communities (Godwin, 1994). The institutional memory may keep a record of how the individuals in the community behaved in the past, forming reputations of each member. The importance of the reputation and persistent identity was stated by Kollock (1998, p. 59):
"If identity is unknown or unstable and if there is no recollection or record of past interactions, individuals will be motivated to behave selfishly because they will not be accountable for their actions. Knowing the identity and history of a person allows one to respond in an appropriate manner. If information about the individuals and their actions is shared among the group this also encourages the development of reputations which can be a vital source of social information and control."
Both Kollock (1998) and the workshop report (Whittaker, Issacs, & O'Day, 1997, p. 137) refer to policies regulating the use of shared resources as a central issue.
Godwin (1994) stresses that, the users should confront with crisis. Similarly, Kollock emphasizes the importance of scarcity and risk. Crisis, scarcity, and risks are abundant in the "real world". In most cases collective action is needed to resolve crisis. Such collective action strengthens social ties among the community members. Crisis, scarcity and risk strengthen the bonding among the community.
This study focuses on an online community, Eksisozluk, without any inherent learning goals. Although I do not imply that members do not learn from their experiences in Eksisozluk, we can easily say that Eksisozluk is not an online learning community. At this point it is important to make a distinction between online communities and online learning communities to explicate why Eksisozluk is not an online learning community.
In addition to Selznik's (1996) seven characteristics of a community Schwier (2002) defines three additional characteristics for online learning communities: future, technology and learning. Among these three characteristics "learning" distinguishes an online learning community from an online community. While learning can happen in any community, online learning communities have negotiated common learning goals with shared values defining how learning will occur.
Schwier (2002) defines an online learning community as a type of a virtual learning environment where learners engage each other intentionally and collectively in the transaction or transformation of knowledge. According to this definition not every virtual learning environment is a community. An online learning community should allow its participants to collectively develop ways of constructing knowledge and negotiating meaning within the context of the community.
4. Study Content: Eksisozluk
"Ekşisözlük", a Turkish phrase meaning "sour dictionary" in English, is an online and interactive dictionary encompassing definitions of concepts, entities, and conditions. The medium of the dictionary is in Turkish. Each concept/entity/condition is called a "title" and the definitions written for a specific title are called "entries." Members, who are called "authors", enter about 3000 entries per day. The popular motto of Eksisozluk is "Holy information resource."
Sample/random titles and entries found in the dictionary:
To give a sense of the format, the language, and the general style of the entries, some random examples are provided below. These entries were originally written in Turkish and the translations are represented here.
Newsweek
1) The news magazine similar to Time. The relation between these two can be portrayed as a competition between Big Mac and Whooper.
(set, 04.01.2001 21:41)
15) Do not become a subscriber to this magazine simply because you are attracted to its cheapness. After a couple of issues, you begin to pile it, without even opening its cover; there is not too much to read inside for an average Turk.
(vinyl, 09.02.2004 12:01 ~ 26.02.2004 10:11)
Requirements for pursuing a Ph.D.
1) Generally having strong nerves, patience, self sacrifice and in addition, having a masters degree are prerequisites for most of the programs.
(purplehaze, 18.07.2002 20:04 ~ 20:48)
28) The ability to compress your life into the square of [apartment - department - advisor - Budweiser]
(contraddiction, 06.08.2004 04:10)
OSPF
2) A link state routing protocol that is frequently used in the Internet. It is defined by RFC 1247.
(nt christ, 04.12.2003 02:51)
3) Used for IP. Indeed a link state protocol. Avoids the path information, that may cause a loop, by keeping another topology and transferring those information. It is such a sincere protocol. By saying "hey I am keeping this information in another place but avoiding them at the same", it informs the opposite side. Then the avoided information is used for the calculations made by OSPF to prevent the loop. The subnet information can be transferred by the OSPF protocol. By this facility VLSM provides some additional functionality.
(olympos, 16.03.2004 02:22 ~ 09.06.2004 13:24)
7) A fascist routing protocol in which the one waking up early seizes the governance.
(kimmeryali, 18.03.2005 12:18)
World Bank
6) The bank, founded in 1945, also known as "International Bank for Reconstruction and Development" whose headquarter is located in Washington. One of the specialized organizations of United Nations, the World Bank aims to provide monetary aids to member countries for effective investments, help them develop, facilitate the world trade in the long term, make investments in areas that the private funds are not sufficient.
(risk, 12.12.2002 11:31)
Selected Characteristics of Eksisozluk
To draw a better picture of the community structure of Eksisozluk four characteristics of the community were selected and explained in further detail.
Rating system: Next to the each entry three buttons appear: 1- ":)", 2- ":o", and 3- ":(". The author reading the entry can vote for it using one of these buttons. ":)" is used for a positive vote, where ":o" is used for neutral, and ":(" is used for negative. These buttons are visible only to authors. Based on the votes given, various types of statistical categories are calculated both under the statistics part of the website and under the author information screen.
Identity, Reputation, Member History: Godwin (1994), Whittaker, Issacs, & O'Day (1997) and Kollock (1998) point to the importance of persistent identities and continuity in communication within communities. In Eksisozluk all of the users have persistent identities, represented by a nickname. It is impossible to change the nickname or use two or more nicknames. The search engine, called the "hayvan ara," enables all of the users to make advanced searches on the entries. For example, utilizing the engine, a user can reach all of the entries, the best entries, or the best recent entries of a particular author.. Another facility named "kimdir nedir" which stands for "who is and what is" gives detailed information about the author's reputation, most popular and least popular entries as well as statistical information about entries written by the author.
Communication/Socialization: Eksisozluk website has an internal message facility enabling the site members to send messages to one another. Each member can form two kinds of lists; "badi" (buddy) and "mal" (dumb). The nicknames of the members, on the badi list, are visible on the right hand side of the main frame when they are online. The messages from the members in the "mal" list are blocked. The users can send their comments; express their critics or pleasure about each others' entries via the messaging facility.
In addition, the site members have frequent face-to-face meetings, taking place anywhere around the world. Some of the meetings are activity oriented (e.g., going to concerts, football games, etc.). During these meetings, the members advertise their nicknames with stickers on their clothes.
The site features a network of internal web sites called Sub-Etha which is only open to site members. The sub-sites are built by independent developers and hosted on different locations. Users logged in to Eksisozluk can visit those sites without requiring additional member registration or logging in. The network includes several sites, for example, an art portal called "Sour-FX", a meeting organization and photo-album page called "SourSummitz", the "Eksi Sozluk Museum", and an external entry backup facility called "SourLemonade" (Wikipedia, 2005).
(4) Statistics: In the statistics part of the website, there are various categories, some of which worth mentioning here (Table 1) (Eksisozluk, 2008).
Table 1. Some selected statistics regarding Eksisozluk
| General Statistics | Location of authors | Number of entries in years | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
Other than the ones presented here there are 30 more categories of statistical data, including the most popular authors, the mostly liked entries of the week, the worst entries of the week, and the most successful proditors.
5. Methods of Inquiry
This study utilized a collective case study design (Merriam, 1998; Stakes, 2000; Yin 1994). A "case" under investigation is an "active Eksisozluk author".
The following research questions guided the investigation of this study:
(1) Which factors in Eksisozluk motivate authors to contribute?
(2) Which of the design principles and characteristics of Eksisozluk can be applied to online learning environments to facilitate learning and increase motivation?
Study data were collected through surveys and interviews. The survey items were selected to inquire the extent to which the structural and emergent characteristics of Eksisozluk influence the participation and motivation of the survey participants. After having the approval from the Human Subjects Committee at Indiana University, Bloomington, the study was announced at the community website (http://www.sourtimes.org) under the announcements section. Members, who have been interested in participating in the study, followed the link provided at the announcement to complete the survey and submit their emails addresses for having contact for the interviews. For the survey, 877 participants and for the interviews, 3 participants volunteered. Survey participants were directed to an online questionnaire. They responded to 20 questions. Participants for the interviews were contacted via the email addresses they provided. After the contact, researcher and the participants negotiated for the dates to conduct the telephone interviews. Each phone interview took approximately 30 minutes. Phone interviews were recorded with a digital sound recorder. The recorded conversations were transcribed. The audio files for the interviews were deleted after the transcription.
In the survey, participants answered two main questions:
-
Please rate the extent to which the following are important in your involvement in the Eksisozluk community.
-
Please rate the extent to which the following characteristics of Eksisozluk attract your participation.
There were sub-categories under each question. Respondents rated their views regarding those sub-categories using a five point Likert-scale. The sub-categories can be found in the appendix.
In the interviews the participants answered three sets of questions. The first set of questions focused on the authors' perceptions and experiences about their learning in the community. The second set focused on their perceptions of Eksisozluk as an entertainment source/tool. The third set of questions was about how they socialize in Eksisozluk and how socialization relates to their learning.
6. Findings
Surveys
Participants' average ratings to survey items were computed. In Figure 1, the average ratings to the sub-categories of the first item are listed. "To learn something" appeared to be the main motivation for the participants' involvement in the website (4.15 out of 5). Second highest rated motivation factor was to "share information" (4.01 out of 5). Average response rate for "fun and entertainment" was 3.79, which is also a close rating to the other two highest rated factors. The factor "to socialize with others" was rated significantly lower than the other three (2.49).
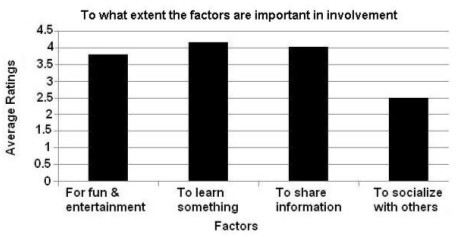
Figure 1. Which factors are important in authors' involvement in Eksisozluk
In the second question, the characteristics of Eksisozluk that attracted participation were asked to be rated in a Likert-scale These characteristics were grouped into two: (1) "Structural characteristics" (Figure 2) and (2) "Emergent characteristics" (Figure 3). The first group includes characteristics that were predetermined and intended by the developers. The second group includes characteristics of Eksisozluk that were not primarily designed or intended by the developers of the website, but emerged through time.
Participants rated "Users form the content" (4.4/5.0) and "No cost of use" (4.0/5.0) as the two most important structural characteristics. "Unlimited entry length" (2.4/5.0) and "Different set of statistics" (2.3/5.0) were rated as the two least important structural characteristics.
"Continuously increasing content" (4.4/5.0) and "Presentation of multiple perspectives" (4.0/5.0) were rated as the most two important emergent characteristics, where "number of members (authors)" (2.3/4.0) and "number of readers" (2.3/4.0) were rated as the two least important ones.
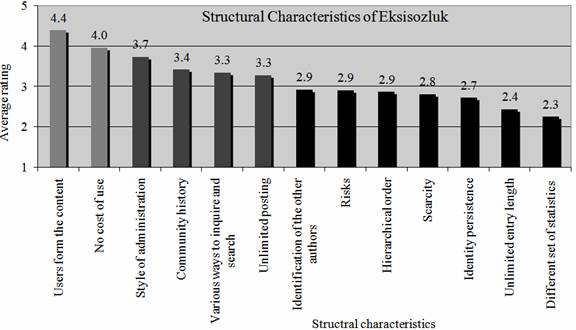
Figure 2. Structural characteristics of Eksisozluk
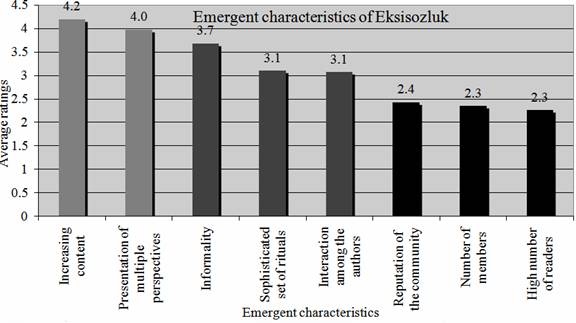
Figure 3. Emergent characteristics of Eksisozluk
Interviews
I conducted interview with three participants. Findings from each interviewee are presented below.
1st Interviewee (Aslı): The first interviewee was a 30 year old female, working on her PhD at a major university in Ankara, Turkey. She has been an author in Eksisozluk since 2004.
In the interview, Aslı said that she does not use Eksisozluk (will also be referred as "the dictionary" from there on) for academic research. She rather uses it to learn about daily issues, news, culture, history; anything she wonders about. She thinks that Eksisozluk is different from the other resources on the Internet because, although the authors have subjective points of view, the structure of the community often results with a neutral representation of knowledge. She stated that most resources on the Internet represent a particular point of view, but Eksisozluk provides the ground for the representation of multiple perspectives in a balanced way. Although people represent different, sometimes opposite, points of view, members and the administration of the community agree to disagree. She believes the search facility, "Hayvan ara", is the primary interface, which facilitates her learning. She pointed out that it is very important for her to be able to search for certain authors' entries, with a reputation in certain topics, for example "cinema." She said that "Everything happens in Hayvan ara." When asked about a specific experience for learning in Eksisozluk, she said that she follows the news from the dictionary, and, for example, when she was pregnant, she read about pregnancy and learned many valuable things. Nevertheless during her readings about pregnancy she realized how much the community was dominated by young males. To reverse this pattern, she started doing research and contributing to the content regarding pregnancy and childcare, from a mother's perspective. She thinks that although the structure of the dictionary facilitates neutrality, the author profiles are not representative of the society. She also said that the "buddy mechanism", which allows the authors to add certain authors in their buddy list and communicate with them privately, facilitates learning, which takes place during private, on to one, conversations with the "buddy authors": Referring to the advantages of private conversations with other authors, she said "Sometimes they share things that they don't write in their entries."
Aslı did not view Eksisozluk as an entertainment website, although she found some entries, especially about soccer games, funny.
While talking about her socialization experiences in Eksisozluk, Aslı said she is in contact with a couple of authors who are living in Ankara and are also mothers like her. In addition, she has friends from the community with different backgrounds. She emphasized that Eksisozluk provides different ways of getting additional information about other authors, such as reading their entries and checking their "who is who" pages, before having any personal contact with them, either online or face to face. She compared ICQ and MSN to Eksisozluk and maintained that while people are just nicknames in an instant messaging program, in Eksisozluk authors express themselves with their unique views in a variety of subjects, with their "who is who" pages leading to a better understanding of the author's personality and world view. To exemplify some of the social experiences she had in Eksisozluk she said that she is discussing some issues about French language with one of the authors, and exchanging information about childcare with another one. She added that she and her friends from Eksisozluk are even planning to meet face to face some time but they could not schedule it because both are very busy with their jobs.
When asked how she would describe Eksisozluk the most; as a medium of learning, entertainment or socialization, she stated that she would describe it as a medium of "muhabbet" (roughly means conversation). For her it does not fill any of the categories completely: "Eksisozluk is a source of information, but I receive knowledge from it: I decide what I get. I read the entries of whomever I find worthy. This is the social part; there is a selection in it. Entertainment plays role in the readers and the authors' motivation of participation in the community."
2nd Interviewee (Murat): Murat is a 28 years old PhD student of cognitive science, living in Ankara, Turkey. He is also employed in the computer center of the university at which he is pursuing his PhD. He has been an author in Eksisozluk since 2002.
He stated that he looks up for information about his research topics in Eksisozluk. He uses Eksisozluk as frequently as he uses Google. When he cannot find information about a specific topic in Eksisozluk, he searches for it in either Wikipedia or Google. He also uses the dictionary for academic research. Murat said that he used Eksisozluk even during his PhD qualification exam preparations..
He thinks that Eksisozluk has some commonalities with some other resources in the Internet in the way it includes encyclopedic and factual information. In addition to such "classic" information, it includes commentaries reflecting authors' subjective points of view. People share their personal experiences and perspectives. Authors write things that a person would say in a personal conversation. He thinks that he reaches to some private information.
Murat does not find the reliability of information in Eksisozluk satisfactory. He finds it acceptable to read different authors' conflicting and often speculative entries Although Eksisozluk is not the first resource for Murat to check for "objective" or "scientific" information, in many cases he enjoys authors' original perspectives on scientific issues. Murat thinks that Eksisozluk is quite satisfactory in terms of originality and representation of multiple perspectives.
Murat expressed that the search facility is the key for reaching the desired information. The search facility helps him watch the entries of his favorite authors. To facilitate learning in Eksisozluk, Murat proposed writing identifiable and critical "objective" and "factual" entries first, and the more subjective entries next, under the same title. Unlike Aslı, Murat uses Eksisozluk for academic research. He learned a lot of things relevant to his academic field of study from Eksisozluk that he would not have learned otherwise, from his graduate level college classes.
Murat thinks that the rating system in Eksisozluk increases motivation. Authors, knowing that their entries will be evaluated by other authors and readers, struggle harder to attract people's attention. In addition, the risk of being dismissed makes them more diligent about conforming to the "format," the regulations on how to write the entries. Although there is almost complete freedom on the content, according to the "format" an entry written under a title should define the title.. Murat compared the motivations of authors in Eksisozluk to the students' motivation in a college class: While the context and the subject of discussion is predetermined in a class, in Eksisozluk it is the authors who decide what they want to discuss, whether it is politics, history, or cognitive science. "You decide on the goal of being there." According to Murat humorous and informal style of writing also increases motivation. He believes that the content is more readable, no matter what the topic is about, especially when it includes humor in a balanced way.
In terms of socialization Murat stated that Eksisozluk has the advantage of both sustaining a persistent virtual identity for each author but at the same time providing ways of staying anonymous, since members do not necessarily publicize their personal information.
3rd Interview (Meryem): Meryem is a 28 years old female graduate student pursuing a PhD at a north American university. She has been an author in Eksisozluk since 2002.
She uses Eksisozluk to lookup meanings of words from different languages, or to find information about anything, except her academic field, which is molecular biology. She does not find the information provided in Eksisozluk reliable enough to use it as an information resource for her academic studies. She believes that HYPERTEXT structure, being able to jump from on entry to another, and the search facility make Eksisozluk an effective learning tool.
Meryem believes that the language used in the dictionary increases the motivation of both the authors and the readers. The informal writing style makes the content of Eksisozluk easier to understand and gives the feeling of a conversation instead of simply reading an encyclopedia like resource.
Meryem refers to Eksisozluk as a unique medium for socialization on the Internet, in the way members have the chance to learn about other people and their ideas on a large variety of topics before they have any personal contact.
7. Implications for Practice
What are the factors of Eksisozluk that motivate the authors to contribute?
Considering the high engagement levels, the factors that motivate the participation to Eksisozluk are worthy of consideration. Sustaining student motivation is a challenge in online learning environment design. During the data collection participants of Eksisozluk appeared to be considerably motivated. Murat, an interviewee, expresses his motivation: "Whenever I have some spare time during the day, I enter the website, read or write entries,". This high motivation can be due to the both structural and emergent characteristics of Eksisozluk that are discussed in this section.
The survey results show that "users form the content" is the most important structural characteristic in terms of motivation. This enables the dictionary to continuously be updated with new information. There is always something new to read. Because of the added content, the dictionary is also continuously expanding. The increase in content was rated as the most important emergent characteristic. Interviewees also favored this characteristic. Aslı and Murat stated that they were using the dictionary to learn about the daily news. As the authors act like reporters who are gathering information from multiple news resources, including news portals, forums, blogs etc., and carrying these information into the community, Eksisozluk becomes a new portal in which the news are updated almost real-time. This dynamic nature of the community motivates the readers and authors to visit the website frequently.
"Presentation of multiple perspectives" was rated as the second most important emergent characteristics of Eksisozluk. All three interviewees mentioned that diversity and representation of multiple and often conflicting perspectives are important assets of Eksisozluk. Aslı mentioned that she especially liked having conversations with people, via the message facility, who had opposing points of view in subjects she is interested in. She also mentioned that she found it very useful to read the entries of people who are specialists in certain fields. These people contribute to Eksisozluk by carrying their professional knowledge to the community. She gave some examples on how she learned more about pregnancy, childcare and some legal issues by reading entries of different people who were specialists in medicine, early childhood education, and juristical issues. Murat mentioned that he read entries and discussed some issues with other authors in philosophy of cognitive science and cognitive linguistics during his PhD qualification exam preparation studies. He stated that he especially found valuable information about the Newcomb paradox and the Chinese room argument. With its diverse, highly contributing authors, Eksisozluk does not confine itself to the accumulation and representation of knowledge from a certain perspective or in a specific subject or field. The diversity of participants results with diversity in content.
Informality in the community was rated as the third most important emergent characteristics. Murat mentioned that the informal style of writing made it easier to read and understand the entries. Although some titles are about scientific topics or academic issues, authors often use an informal language in their writing instead of an academic style. The entries are also generally humorous. According to Murat, ninety percent of the entries written are humorous no matter what they are about. For him this informal and humorous style facilitates learning.
Style of administration came out to be the fourth most important structural characteristics of Eksisozluk, according to the surveys. Although the administration of the community is not really democratic, they are continuously communicating with the authors through the message facility, and taking their views and comments seriously. The administrators are at the same time authors. Murat defined the administration as "anti-democratic," although they still listen to authors' varied views.
Community history is one of the core attributes of an online community (Whittaker, Issacs, & O'Day, 1997). Facilities and interfaces for keeping track and sharing the history of a community is likely to have positive effects on users' motivation . In Eksisozluk history of an author constitutes entries written, interactions with other authors and statistics, which altogether support a persistent identity. Persistent identities help authors and readers have permanent social links that develop and get more comprehensive with time. Persistent identities also help to form reputations. Murat and Aslı mentioned that, having some knowledge of an author by reading her entries and checking her "who is who" page, facilitates social interaction: "It is easier to communicate with someone if she is not only a nickname for you" said Aslı. Although the users have persistent identities, they do not have to share their real identity in Eksisozluk. Murat emphasized this as one of the characteristics of Eksisozluk that facilitates social interaction: "I want to meet people and discuss things online and continue my interaction through time, but at the same time, I want to be anonymous. Eksisozluk provides both of these."
During the interviews, all three interviewees emphasized the importance of the search facility. Aslı referred to the search facility as the "core" attribute of the website. In the surveys "various ways to search" was rated as the fifth most important structural characteristic. Ease of finding the needed and desired information affects user motivation. For Murat, the search facility functioned like a filter, because it let him search for the entries of specific authors under specific titles, which also let him avoid seeing unnecessary and unwanted information.
Godwin (1994) represents "unlimited posting" as one of the nine characteristics of a good online community. In Eksisozluk the authors are allowed to post unlimited number of postings in unlimited length. This characteristic was rated as the sixth most important structural characteristic, in the survey.
Interaction among the authors is an important attribute of an online community. This characteristic was rated as the fifth most important emergent characteristic, in the survey. Aslı told me that, during a private communication with other authors, through the messaging facility or the buddy list interface, she learned things that she could not have read otherwise in the entries. She pointed out that, during interactions with other authors she had access to "customized" information and answers to specific questions. Meryem said that she had some friends in the community that she discussed certain subjects, for example issues regarding the French language and molecular engineering, particularly with authors who were specialists in these fields. All three authors highlighted that, communication with other authors was more appealing in Eksisozluk, compared to other online environments, because they had access to detailed information about other authors before having any personal contact. Murat said that he felt more comfortable communicating with other authors when he knew some background information in terms of the other party's perspective on a variety of issues.
Being an author in Eksisozluk includes many risks: (a) the authors' entries may get bad ratings, resulting with a low reputation, (b) entries not conforming to the format can be deleted, and the authorship can be suspended for a limited amount of time, or (c) the author can be banned from the website if she insults someone or writes something violating the laws. Murat believes that, risks presented in the community direct people to write higher quality entries. He said "… people want to convey their ideas and want to be appreciated. The rating system drives them to strive to write higher quality entries, so that their ideas can be appreciated or attract some attention."
While the above characteristics of Eksisozluk appeared to motivate the authors, the interviewees pointed out some factors that impede their motivation. Murat stressed that some authors write entries with a dry and superficial understanding of humor and without giving any information about the title they were written under. He believes that, especially the new authors dominate the dictionary with irrelevant, absurd, and misleading entries, to attract attention. He proposes that the administration order the entries under the titles so that information giving ones can be reached first. Both Meryem and Murat mentioned that they do not want to see "trashy" entries while they are seeking for specific information in the dictionary.
Although Eksisozluk does not, directly, intend to be an online learning environment many of the characteristics it encompasses can be applied to online learning environments to help increase motivation and facilitate meaningful learning. The lessons learned from Eksisozluk that can be transformed to applicable design principles are discussed in the next section.
Which of the design principles and characteristics of Eksisozluk can be applied to online learning environments to facilitate learning and increase motivation?
High number of authors contributing to an online community creates a dynamic environment where new information is constantly added. In an online learning environment, for example in a course management system, contribution should not be limited to students who enrolled in that particular course. The forums and other resources could be open to outside participants, for example to other students in the department the course is offered. Information accumulating in an online learning environment can be stored and made available to everyone even after the course is over.. Course management systems can be restructured in a way that information created in consequent semester of the same course can accumulate. In this way current students of a course can connect their learning and research efforts to what has been done in the course by other students.
Alternatively, online course websites can be situated in public online communities.. One advantage of using an existing public online community would be the ease of attracting outside, non-student, participation. In summary, this model considers an online learning environment as a place situated in a larger social sphere with participants with different roles, instead of only students, where knowledge created and history of participants' interactions accumulate throughout time, instead of being reset every semester. The knowledge accumulated and histories of participants' interactions in online learning environments, particularly in course management systems, are valuable and should not be considered as unworthy.
Students taking an online or blended residential-online class may not be as diverse as it would be desired in terms of their fields of study, interests and academic backgrounds. Representation of multiple perspectives in a course encourages ideas to be challenged, discussions to be initiated, and different perspectives to coevolve through insightful discussions. According to the present study findings, an online community attracts higher level of participation as more diverse and conflicting perspectives are represented.
A structural change to increase the participation and allow the representation of multiple perspectives might be to remove the boundaries among different communities of students taking different classes. In this model, discussions, forums, and resources should not be categorized under classes, but under different topics.
Feedback provided by the students and the faculty should be taken into consideration to support the efforts of designing and further improving an online learning environment. This, in turn, could help students develop a feeling of commitment to their practices and an ownership of the environment they are engaged in. It could also provide them with the opportunities to express problems that impede their learning. Generally a development team designs the online learning environments and students are expected to learn how to use the interfaces and facilities provided. Indeed, the design of the online learning environment should be an ongoing process where the user feedback is utilized to continuously improve the environment. This would be a co evolution that is realized in the feedback loop including the students, faculty, design and development team, and the stakeholders. An online learning environment should not be a place where only students are expected to adapt to the environment. The environment should also change based on the students' needs.
Community history and identity persistence are two important assets that most online learning environments lack. Social interaction is easier when two parties know more about each other before the interaction takes place. To have a community history, the learning environment should be structured in a way that information accumulated does not erode at the beginning of each semester. Each course should not be considered as a new start. Just like students have a history of academic experiences before they come to the course, the course also has history with different students and instructors. In this sense, both the course and students should bring their history together. This can only happen if the course management system is restructured to allow such continuity of history. Through a search interface students could access to the history of other students; their postings, other people's comments to their postings, their reputation, etc. Kollock (1998) regards individual history as one of the characteristics of a successful online community "Individuals must have information about how the other person has behaved in the past." By doing so, postings of the authors (or students) could be easily accessible, other people's comments about them could be presented in a separate page, and their reputations, which are rated based on the quality of their written contributions could be publicized in the community. As postings of people are manifestations of their perspectives, students can reach to previous postings of other students before initiating any discussion. This may avoid repetition of similar discussions, and help initiate further discussions. Another structural principle that can be applied is to let students modify some of their old postings, similar to a Wiki environment, based on changes in their perspectives. In this regard postings are not temporary, one time declaration of ideas but rather long term manifestations of students' perspectives.
An effective, usable search facility is very important so that information and postings belonging to a particular student can be accessible or postings can be inquired for certain topics or subjects.
To foster the interaction among the students, in addition to public posting facilities, they should be provided with private chat and messaging facilities. These facilities may help students have some more private interaction.
According to present study findings and Godwin (1994) risks presented in an online community motivate participation and a higher quality of contribution. Often in online learning environments the only risk presented is receiving a low grade. Students are not evaluated by their colleagues based on their contribution to the learning community. This can be improved by maintaining a reputation score of every student, which is calculated by the ratings of other students, not only during a specific course but throughout students' studies during the degree program.
8. Study Limitations
The survey for this study was announced in the Eksisozluk community website by the administrators. Although this announcement was received by only the authors, there was no way to ensure that everyone filling the survey was an author. As authors prefer to keep their anonymity, I could not ask them to provide private information for authentication. The number of interviewed authors constitutes another limitation. Considering the high number of authors and the wide range of diversity they represent, interviewing more authors could have provided more insightful results in understanding the dynamics of Eksisozluk.
9. Conclusion
Eksisozluk is not an online learning community. Nevertheless, it is a place where people socialize, learn and entertain themselves at a level desirable in online learning communities. A community history, persistent identity of authors, increasing content in diverse fields and topics, high number of readers and effective tools for searching for and filtering information are some of the characteristics of Eksisozluk that have the potential to improve and transform online learning communities. Further research on other successful online communities, for example Wikipedia, may give additional clues as to how we should design online learning environments to increase participants' motivation and allow meaningful learning experiences.
References
[1] Eksisozluk (2008). Eksisozluk Statistics. Retrieved December 14, 2008 from http://sozluk.sourtimes.org/stats.asp
[2] Etzoni, A., & Etzoni, O. (1999). Face-to-face and computer-mediated communities, a comparative analysis. The Information Society, 15, 241-248.
[3] Godwin, M. (1994). Nine Principles for Making Virtual Communities Work. Wired, 2(6), 72-73.
[4] Huang, H. M. (2002b). Toward constructivism for adult learners in online learning environments. British Journal of Educational Technology, 33(1), 27-37.
[5] Kollock, P. (1998). Design principles for online communities, PC Update ,15(5), 58-60.
[6] Merriam, B. S. (1998). Qualitative research and case study applications in education. San Francisco, CA: Jossey-Bass Publishers.
[7] Preece, J., & Maloney-Krichmar, D. (2003). Online Communities. In J. Jacko and A. Sears, A. (Eds.) Handbook of Human-Computer Interaction, Mahwah, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates Inc. Publishers.596-620.
[8] Schwier, R. (2002). Shaping the Metaphor of Community in Online Learning Environments. Unpublished Manuscript, University of Saskatchewan
[9] Selznick, P. (1996). In search of community. In W. Vitek & W. Jackson (Eds.), Rooted in the land (pp. 195-203). New Haven: Yale University Press.
[10] Smith M, Kollock P, eds. 1999. Communities in Cyberspace. London: Routledge
[11] Stakes, R. E. (2000). Case studies. In Denzin N.K. and Lincoln Y. S. (Eds.), Handbook of qualitative research, Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publishers.
[12] Whittaker, S., Issacs, E., & O'Day, V. (1997). Widening the net. Workshop report on the theory and practice of physical and network communities. SIGCHI Bulletin, 29(3), 27-30.
[13] Wikipedia, (2005). "Eksisozluk", Retrieved April 8, 2005, from http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Eksi_Sozluk
[14] Yin, R. K. (1994). Case study research, design and methods. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications.
Appendix
Sub-categories for Survey Questions
In the first question, the user's main motivation for entering the site was explored. The categories presented under this first question were:
For fun & entertainment
To learn something
To share information
To socialize with others
The participants were expected to grade these categories on the following scale:
Not at all important |
Not very important |
Somewhat important |
Very important |
Extremely important |
In the second question different characteristics of Eksisozluk were provided as categories, to understand which of these characteristics had positive effects in the user participation in the online community. The categories listed were:
High number of readers
Number of members (authors)
Reputation of the community
Identity persistence
Sophisticated set of rituals
Interaction among the authors
Various ways to inquire and search for entries (i.e., the internal search engine with various capabilities, lists)
Use of different set of statistics to classify the entries and the authors (most popular entries of the week, best authors of the year etc.)
Identification of the other authors (a result of identity persistence and channels for interaction among authors)
Community history
Unlimited posting
Unlimited entry length
Hierarchical order
Style of administration
Informality
Risks (i.e., punishments and the risk of having a low reputation)
Scarcity (Difficulty of being an author, difficulty of having a high reputation)
Presentation of multiple perspectives
Continuously increasing content
Users form the content (self-feeding web site)
No cost of use
The participants were expected to grade these categories on the following scale:
Not at all important |
Not very important |
Somewhat important |
Very important |
Extremely important |

